Sporos BioDiscovery’s Diversified Pipeline
Using a genetically-validated framework, Sporos generates key biological insights into tumor-specific vulnerabilities and their symbiotic interactions across the broader tumor microenvironment. This approach provides a FULL picture of each cancer and how to develop therapeutic candidates that may improve outcomes and quality of life for patients.
IN VIRTO DISCOVERY
IN VIVO PRECLINICAL
POC IND
ENABLING PHASE I
PROGRAM
SPR1
Precision Oncology
PHASE
IND Enabling
PROGRAM
SPR1
Precision Oncology
PHASE
IND Enabling
Target: TEAD
Focus: Cancers with Hippo-driver mutations / aberrations and YAP/TAZ hyperactivation
TARGET
TEAD
FOCUS
Cancers with Hippo-driver mutations / aberrations and YAP/TAZ hyperactivation
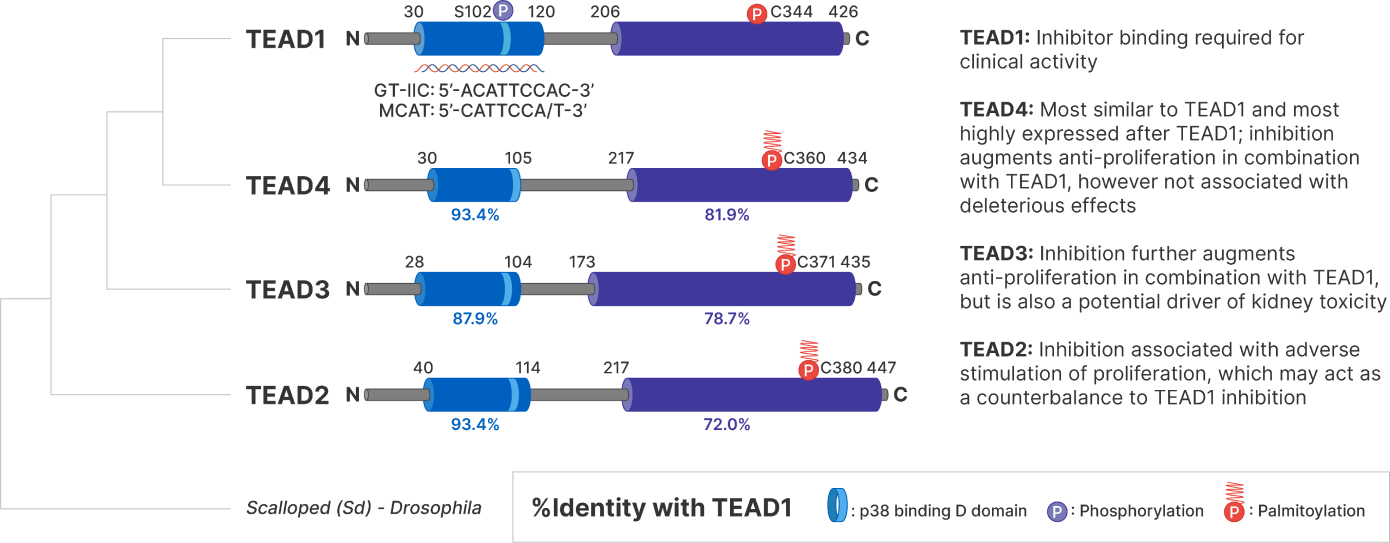
SPR1 is a novel small molecule, isoform-selective inhibitor of TEAD1 / TEAD4. SPR1 targets cancers driven by mutations in the Hippo pathway, a key regulator of cell proliferation and oncogenesis not yet extensively targeted in precision oncology. The YAP1/TAZ co-activators and the TEAD family of transcription factors, which consists of four paralogs (TEAD1-4), execute the pro-cancerous effects of the Hippo pathway through transcription of pro-proliferative and anti-apoptotic genes. Hippo pathway activation has also emerged as a key mechanism of resistance to inhibitors of the MAPK pathway, making TEAD inhibitors a prime candidate for combination therapy with therapeutics targeting the MAPK pathway.
PROGRAM
SPR4
Precision Oncology
PHASE
Discovery in Vitro
PROGRAM
SPR4
Precision Oncology
PHASE
Discovery in Vitro
Target: Undisclosed
Focus: PTEN-deficient cancers
TARGET
Undisclosed
FOCUS
PTEN-deficient cancers
SPR4 is a small molecule targeting PTEN-deficient cancers. Genetic deletions of PTEN are mutually exclusive in human tumors and simultaneous genetic deletions of PTEN prevents PTEN-null tumorigenesis. Our undisclosed target for PTEN-deficient cancers plays a role in reversing immunosuppression and may synergize with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
PROGRAM
SPR2
Tumor Biology / TME
PHASE
Discovery in Vitro
PROGRAM
SPR2
Tumor Biology / TME
PHASE
Discovery in Vitro
Target: CXCR2
Focus: Cancers resistant to immunotherapy
TARGET
CXCR2
FOCUS
Cancers resistant to immunotherapy
SPR2 is a small molecule inhibitor of CXCR2, which prevents recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) thereby removing impediments of checkpoint blockade immuno-therapies. MDSCs are critical negative regulators of anti-tumor immune response and tumors with high levels of infiltration by MDSCs have been associated with poor patient outcome and resistance to therapies.
PROGRAM
SPR3
Tumor Biology / TME
PHASE
Discovery in Vitro
PROGRAM
SPR3
Tumor Biology / TME
PHASE
Discovery in Vitro
Target: CCR2
Focus: Cancers resistant to MAPK inhibition and / or to immunotherapy
TARGET
CCR2
FOCUS
Cancers resistant to MAPK inhibition and / or to immunotherapy
SPR3 is a small molecule inhibitor of CCR2, a druggable chemokine receptor that forms lynchpin in a signaling cascade that allows KRAS inhibition bypass through recruitment of MDSCs. CCR2 is a major signaling node for the conversion of neutrophils into anti-tumor immuno-suppressive MDSCs.Through significant bioinformatic analysis, we have identified TEAD1 and TEAD4 as the most critical paralogs to inhibit to maximize anti-tumor activity and minimize toxicity.
SPR1
Through significant bioinformatic analysis, we have identified TEAD1 and TEAD4 as the most critical paralogs to inhibit to maximize anti-tumor activity and minimize toxicity.
SPR1 is a first-in-class TEAD1 and TEAD4 inhibitor, which has demonstrated improved single agent preclinical activity, both in vivo and in vitro, compared to other TEAD inhibitors in development, particularly those targeting primarily TEAD1.
SPR1’s unique TEAD1 / TEAD4 selectivity profile has demonstrated broader preclinical activity than other TEAD inhibitors in development across many cancer cell lines that harbor Hippo pathway aberrations. Cancers such as mesotheliomas, of which over 80% harbor a Hippo pathway mutation, and squamous cell carcinomas of the lung, head and neck are all cancers that commonly have Hippo mutations.
In addition to broader preclinical activity in Hippo-mutated cancers, SPR1 has demonstrated strong activity in cancer cell lines where YAP is shown to be hyperactive in the nucleus of cancer cells; however, no Hippo aberrations have been detected. This points to the broad potential for SPR1 as monotherapy across a wide array of cancers that current TEAD inhibitors in development are so far unable to address.
The Hippo Pathway & TEAD
The Hippo pathway is a major regulator of cell number and tissue density. It plays a key role during embryogenesis, and modulates genes responsible for proliferation, differentiation, organ growth, as well as tissue homeostasis.
TEAD is a family of four transcription factors that execute the Hippo pathway. These four TEAD paralogs have both redundant and distinctive functions, some of which have pro-proliferative effects on cancer and some of which have anti-proliferative effects.
Mutations in the Hippo pathway can cause activation of YAP/TAZ –TEAD transcription and are associated with the hallmarks of oncology.
The Hippo and MAPK Pathways
With the MAPK pathway sharing a number of overlapping proliferation, self-renewal, survival, and immune genes, Hippo pathway activation has emerged as a key mechanism of resistance to inhibitors of the MAPK pathway.
Combination therapy of TEAD inhibitors with MAPK pathway drugs offer opportunity for greater efficacy. To date, SPR1 has demonstrated strong synergy with drugs targeting the MAPK pathway and its upstream components, such as KRAS, MEK, EGFR, and FGFR inhibitors.
For this reason, Sporos BioDiscovery is focused on optimizing the inhibitory profile across these four TEADs is to create a best-in-class therapeutic candidate.